Understanding Consumer Behavior in Marketing: Patterns, Types, and Segmentation
Nov 8, 2023
Why is Consumer Behavior Important?
Consumer behaviour plays a pivotal role in determining a business's success in the competitive world of marketing. It comprises the actions and decision-making processes undertaken by individuals when they buy products or services. This understanding empowers businesses to customize their marketing strategies and design products that resonate with their target audience. Without such insights, companies risk missing opportunities, misallocating resources, and failing to foster meaningful relationships with their customers.
Types of Consumer Behavior
Consumer behaviour can be classified into four primary types, each characterized by distinct purchasing patterns and decision-making processes:
Complex Buying Behavior: This category comes into play when consumers face high involvement and significant risk in their purchase decisions. They engage in extensive research, seek recommendations, and carefully assess their options. Examples include buying a new car, a house, or expensive electronic gadgets.
Dissonance-Reducing Buying Behavior: Consumers exhibit this behaviour when they perceive a moderate level of risk in their purchase decisions. They may not delve into exhaustive research but seek reassurance through warranties, guarantees, or return policies. Examples encompass choosing a specific brand of washing machine or smartphone.
Habitual Buying Behavior: This type is characterized by low consumer involvement and minimal risk. Consumers in this category display a strong preference for a particular product or brand and make routine purchases with minimal thought or consideration. Everyday items like toothpaste, laundry detergent, and groceries often fall into this category.
Variety-Seeking Buying Behavior: Some consumers gravitate towards variety-seeking behaviour, which is driven by low involvement and a desire for product variety. They frequently switch between brands, exploring new products and experiences. This behaviour is common in industries such as fashion and fast food, where customers seek diversity and novelty.
What Affects Consumer Behavior?
Consumer behaviour is influenced by various factors, shaping purchasing patterns and decisions. These factors can be broadly categorized into internal and external influences:
Internal Factors:
Psychological Factors: Consumer psychology plays a significant role in shaping buying habits. Motivations, perceptions, attitudes, and beliefs impact decision-making. For instance, a consumer's perception of a brand as environmentally friendly can sway their choices.
Personal Factors: Individual characteristics, including age, gender, occupation, income, and lifestyle, significantly influence consumer behaviour. Demographic segmentation facilitates businesses in targeting specific groups based on these personal attributes.
Social Factors: Social influences, encompassing family, friends, culture, and reference groups, have the power to sway consumer choices. People often seek social approval or align their preferences with those of their social circles.
External Factors:
Economic Factors: Economic conditions such as inflation, income levels, and employment rates directly impact consumer behaviour. Economic downturns can lead to more price-conscious and conservative spending decisions.
Technological Factors: Advancements in technology shape consumer preferences and expectations. For example, the rise of e-commerce has transformed the way people shop, bringing about shifts in consumer behaviour.
Cultural Factors: Cultural values, norms, and traditions exert influence on consumer choices. Businesses must grasp and respect the cultural context in which they operate to effectively market their products.
Customer Behavior Patterns
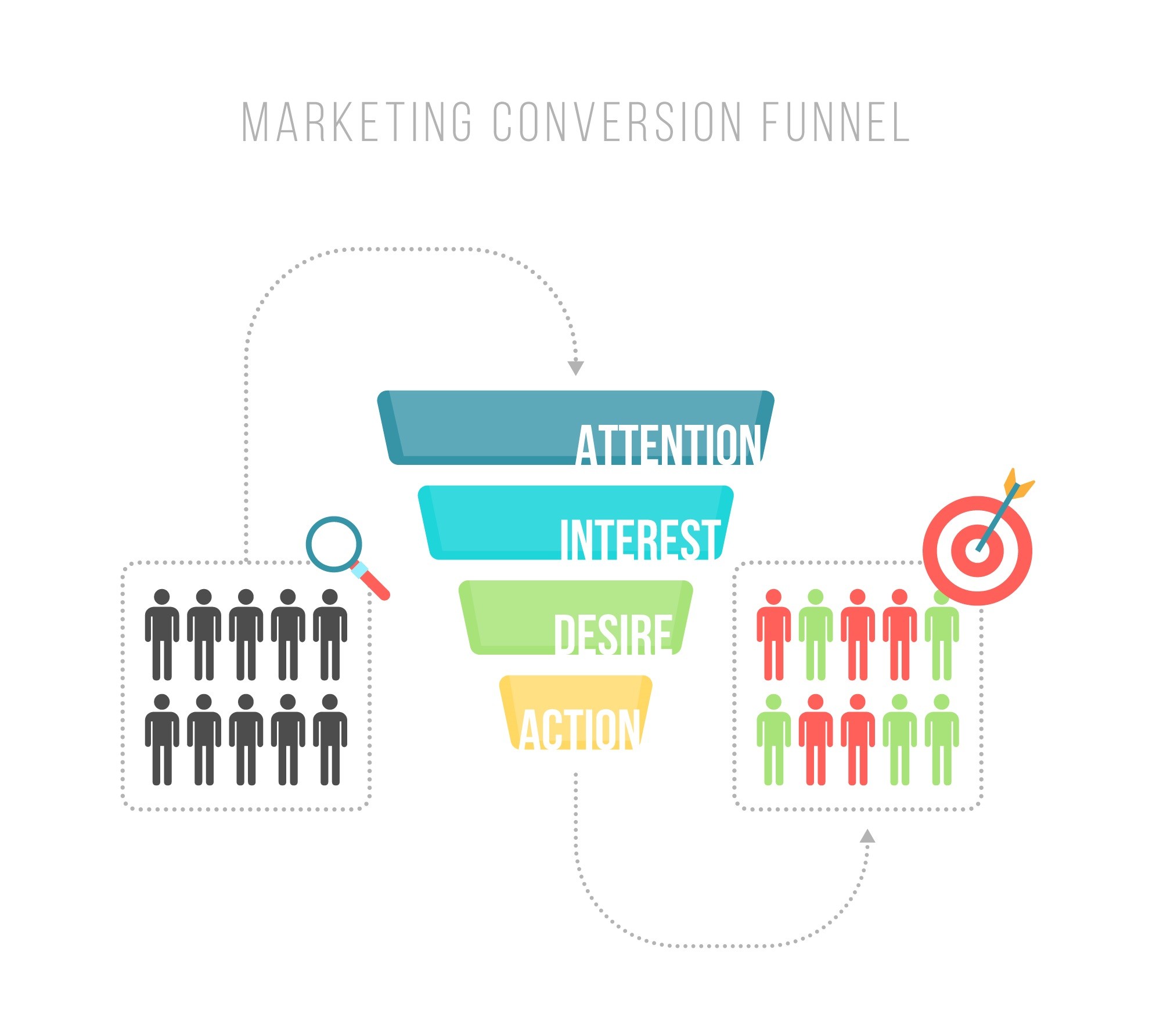
Patterns in consumer behaviour emerge through the analysis of purchase trends and decision-making processes. These patterns offer invaluable insights to businesses seeking to align their strategies with consumer preferences and needs.
Seasonal Patterns: Many products and services experience seasonal fluctuations in demand. For instance, sales of winter clothing surge during the colder months, while beachwear and ice cream sales peak in the summer. Understanding these patterns helps businesses plan their inventory and marketing campaigns accordingly.
Impulse Buying: Impulse buying is a common pattern where consumers make unplanned purchases on a whim. Point-of-sale displays, limited-time offers, and attractive packaging often trigger these impromptu purchases. This behavior is especially prevalent in convenience stores and online shopping.
Brand Loyalty: Consumers with strong brand loyalty consistently purchase products from a specific brand, trusting its quality and being less inclined to switch to a competitor. Businesses with a loyal customer base can leverage this pattern by offering exclusive discounts and loyalty programs.
Word of Mouth: Positive recommendations from friends, family, or online reviews wield considerable influence over consumer behaviour. Businesses can stimulate this pattern by delivering exceptional customer experiences and encouraging satisfied customers to share their opinions.
Customer Behavior Segmentation
Market segmentation is a vital strategy for understanding and targeting diverse consumer groups. It involves dividing the market into smaller, more manageable segments based on common characteristics, needs, and preferences. Here are some common segmentation methods:
Demographic Segmentation: This method classifies consumers based on demographic factors such as age, gender, income, education, and occupation. For example, a children's toy company may target parents with young children.
Psychographic Segmentation: Psychographic segmentation categorizes consumers based on their values, lifestyle, interests, and personality. This approach helps companies forge emotional connections with customers. For instance, a sustainable clothing brand may target eco-conscious consumers.
Behavioral Segmentation: This segmentation method focuses on consumer behavior patterns, including brand loyalty, frequency of purchases, and product usage. A fitness app may tailor its marketing to engage users who work out regularly.
Geographic Segmentation: Businesses can target consumers based on their geographic location, such as countries, regions, cities, or zip codes. Local businesses often use this segmentation to effectively reach nearby customers.
Occasion-Based Segmentation: Some products and services are purchased on specific occasions, like birthdays, holidays, or special events. Companies can segment their market based on these occasions to align their marketing strategies with the timing of these events.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do you mean by consumer behavior?
Consumer behavior refers to the actions, decision-making processes, and purchasing patterns that individuals exhibit when buying products or services. It encompasses the psychological, social, and economic factors that influence these decisions.
What are the 4 types of customer buying behavior?
The four primary types of customer buying behavior are complex buying behavior, dissonance-reducing buying behavior, habitual buying behavior, and variety-seeking buying behavior. These categories reflect different levels of consumer involvement and risk associated with their purchases.
What is an example of consumer behavior?
An example of consumer behavior is when a person decides to purchase a specific brand of coffee because they associate it with premium quality and taste. This decision may be influenced by their psychological factors, personal preferences, and exposure to advertising.
How do you identify consumer behavior?
Consumer behavior can be identified through market research, surveys, customer interviews, data analysis, and observation. These methods help businesses gain insights into consumer preferences, motivations, and purchasing patterns.
What are the characteristics of consumer behavior?
Consumer behavior is characterized by its complexity, the influence of psychological, social, and economic factors, and the variety of patterns, such as impulse buying, brand loyalty, and seasonal fluctuations. Understanding these characteristics is essential for effective marketing strategies.
Why is consumer behavior important?
Consumer behaviour is crucial in marketing because it enables businesses to tailor their strategies to meet the needs and preferences of their target audience. Understanding consumer behavior allows companies to create products, services, and marketing campaigns that resonate with customers, resulting in increased sales and customer satisfaction. Additionally, it helps companies make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and build lasting relationships with their customers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, consumer behaviour in marketing is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various types of buying behavior, influential factors, patterns, and segmentation methods. Understanding and analyzing consumer behavior is essential for businesses seeking to thrive in today's competitive market. By comprehending the motivations and preferences of their target audience, companies can develop more effective marketing strategies, offer products that cater to consumer needs, and establish lasting connections with their customers.
